简介 本文是《玩转Qml》系列文章的第一篇,涛哥将教大家,如何在Qml中实现各种功能的按钮,
同时也会教大家一些组件化编程的思想,如何将做好的功能封装成一个个组件,以便在工程中复用。
写作背景 作者“武威的涛哥”,从2015年开始参加工作,便入手了Qml,参与了很多大大小小的Qml项目,
至今已有五年多实战经验。
2019年,涛哥决定把自己掌握的很多知识都总结整理出来,以《Qml组件化编程》系列文章的形式分享给广大Qml
爱好者和开发者。
涛哥会坚持高质量和深入浅出的原则,将文章写好,让支持涛哥的读者能够受益匪浅。
系列文章中涉及的源代码,绝大部分涛哥都会在github上开源。
如果觉得涛哥写的还不错,还请为涛哥打个赏,您的赞赏是涛哥持续创作的源泉。
有时也难免会犯一些错误,希望看到的读者能够热心指出。有任何相关的问题,也欢迎与涛
哥交流,向涛哥提出建议和意见。
感谢大家!
文章定位 涛哥写的是进阶教程,教大家如何从新手成长为高手,要理解文章中的内容,需要有一点儿Qml基础。
关于基础教程,网络上有很多,涛哥推荐以下几个质量比较高的:
豆子的文章前75章关于Widget部分也很不错。
我眼中的QQuick QQuick使用Qml来描述界面,Qml是可以与html5媲美的存在,其开发效率、舒适度、描述能力和定制化能力已经远远超
过了QWidget,配合各种属性动画、粒子系统和Effects特效可以轻易做出各种酷炫、现代化的UI,不规则的图形可以通
过Painter的方式实现,对于渲染有性能要求的地方可以通过集成OpenGL、Vulkan等图形API的方式来处理。
Qml的特性是自由和灵活,这也是它的缺点,上手Qml需要一小段时间的适应,之后就会大量的造轮子,造的多了就轻车
熟路了,常见的各种二维界面或效果基本上都能造出来。
(当然Qml中也有些bug,需要一定的经验和技巧才能解决。话说回来,哪个框架没点Bug呢?)
再久一点,可以考虑考虑Qml中的设计模式(或者叫惯用手法),如何抽象出通用Qml库、如何最大程度地复用Qml
代码、如何让Qml代码更容易维护等。
Qt版本的选择 Qt发布的版本有很多,一般稳妥的做法是使用LTS(长期支持版)版本的最后一个修正版本。
当前已知的LTS最新修正版本是5.9.8和5.12.3 , 涛哥会优先使用这两个版本,后续有版本
要求的地方,涛哥都会进行额外的说明。
默认按钮 开始进入正题了
Qml中已经有了现成的按钮,在QtQuick.Controls模块中, 目前有两个版本:
1.x的版本是通过style的方式进行定制
2.x的版本则是通过修改Control属性的方式进行定制
2.x版本的默认风格,还可以通过修改配置文件qtquickcontrols2.conf中的style来修改
可参考Qt在线文档- style配置
Qml版本混用 这里顺便说一个经常有人问到的问题: 2.x版本中能否混用1.x版本的控件?
答案是可以。只需要使用别名机制即可。(如果你看过Qml的源代码,就能轻易发现这个用法)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import QtQuick 2.0 import QtQuick.Controls 2.0 import QtQuick.Controls 1.4 as QC14 import QtQuick.Controls.Styles 1.4 as QCS14 Rectange { Button { } QC14.Button { style : QCS14.ButtonStyle { } } }
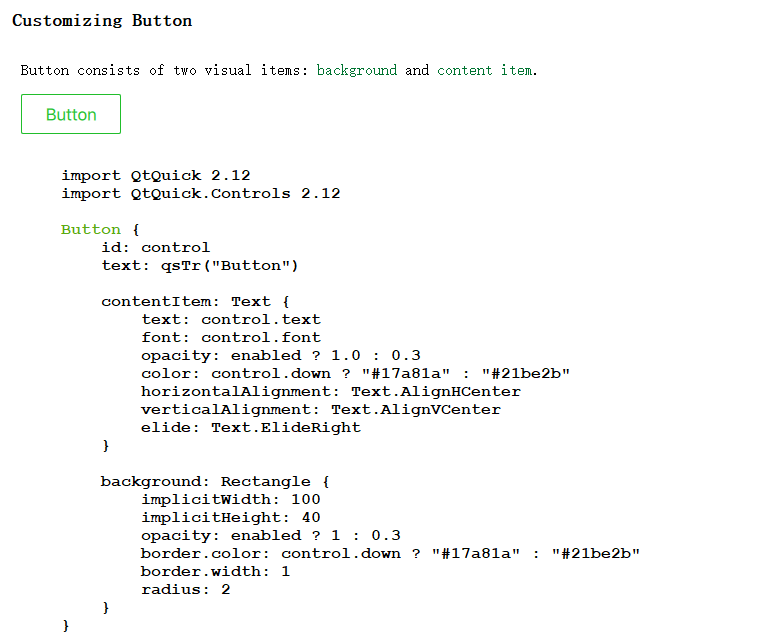
按钮的本质 默认的按钮,很多时候并不能达到想要的效果,比如圆角、贴图片、渐变色的按钮等等,还需要做很多的定制化工作
其实按钮的本质,就是一个可以点击的区域(MouseArea),附带颜色(Rectangle)、图片(Image)或文字(Text)。
涛哥教大家造第一个轮子,一个带文字的按钮。
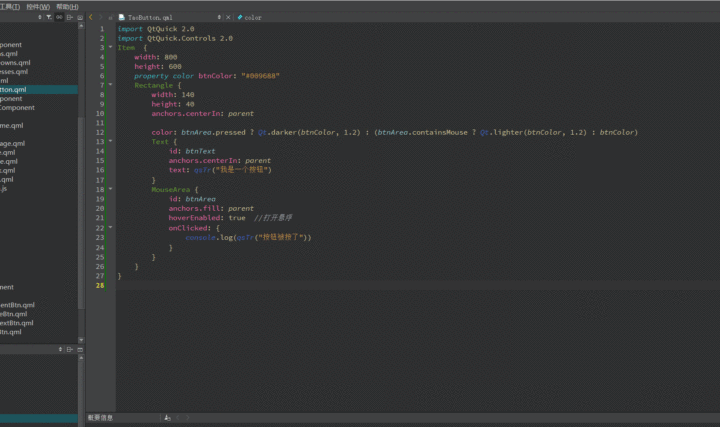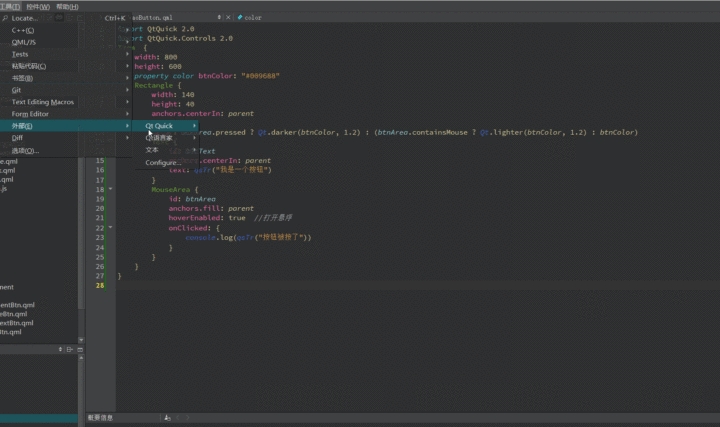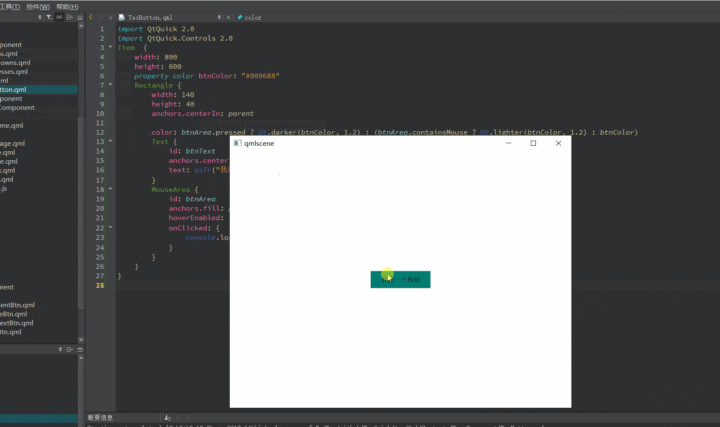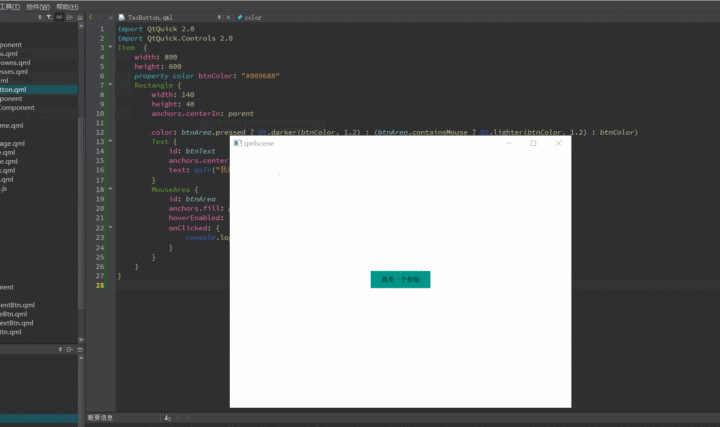
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 import QtQuick 2.0 import QtQuick.Controls 2.0 Item { width : 800 height : 600 property color btnColor : "#009688" Rectangle { width : 140 height : 40 anchors.centerIn : parent color : btnArea.pressed ? Qt.darker(btnColor, 1.2 ) : (btnArea.containsMouse ? Qt.lighter(btnColor, 1.2 ) : btnColor) Text { id: btnText anchors.centerIn : parent text : qsTr("我是一个按钮" ) } MouseArea { id: btnArea anchors.fill : parent hoverEnabled : true onClicked : { console .log(qsTr("按钮被按了" )) } } } }
使用qmlscene预览一下效果
(gif录制工具不能鼠标悬浮,所以悬浮效果看不到,实际上是有悬浮效果的,可自行尝试)
说明一下,qml中有个全局的对象Qt,它有一组调颜色的函数,Qt.lighter和Qt.darker,分别可以按系数来变浅和加深
一个颜色值,这样只要有了一个颜色值,就能自动计算出深一点或者浅一点的颜色,可以减少很多配颜色的工作哦
再看一下这个表达式,当鼠标按下去的时候,使用深一点的颜色,鼠标悬浮的时候使用浅一点的颜色,其它情况就用设定的颜色
1 color : btnArea.pressed ? Qt.darker(btnColor, 1.2 ) : (btnArea.containsMouse ? Qt.lighter(btnColor, 1.2 ) : btnColor)
这里的1.2是试出来的值,也可以使用其它值。
按钮的演变 如果要带个边框呢?只要给Rectange设置边框的宽度和颜色就行了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 property color btnBorderColor : "orange" Rectangle { ... border.width : btnArea.containsMouse ? 2 : 0 border.color : btnBorderColor ... }
如果要圆角呢? 只要给Rectangle 设置radius就行了
1 2 3 4 5 Rectangle { ... radius : 5 ... }
如果要圆形呢?只要给Rectangle设置宽度和高度相等(正方形),radius是宽度的一半即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Rectangle { ... width : 120 height : width radius : width / 2 ... }
如果要背景色做成渐变的呢?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Rectangle { id: gradientBtn ... property color btnColor : containsMouse ? Qt.darker("#009688" ) : "#009688" color : btnColor gradient : Gradient { GradientStop { position : 0 ; color : Qt.darker(gradientBtn.btnColor, 1.2 ) } GradientStop { position : 0.5 ; color : Qt.darker(gradientBtn.btnColor, 1.4 ) } GradientStop { position : 1 ; color : Qt.darker(gradientBtn.btnColor, 1.6 ) } } ... }
顺带提一下,5.12的Rectangle,有了新的渐变色 渐变色网站 ,大约有180种
可以直接在Qml中使用。
1 2 3 4 gradient : Gradient.NightFade gradient : "SugarLollipop"
(gif录制工具不能鼠标悬浮,所以悬浮效果看不到,实际上是有悬浮效果的,可自行尝试)
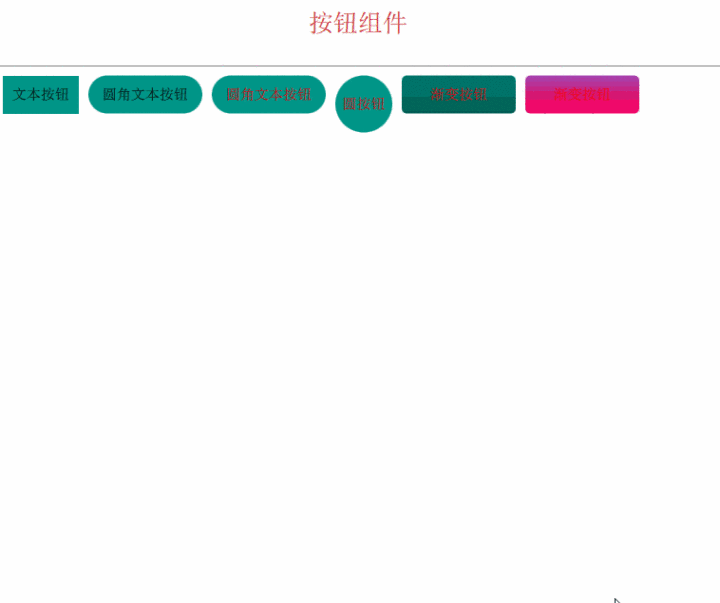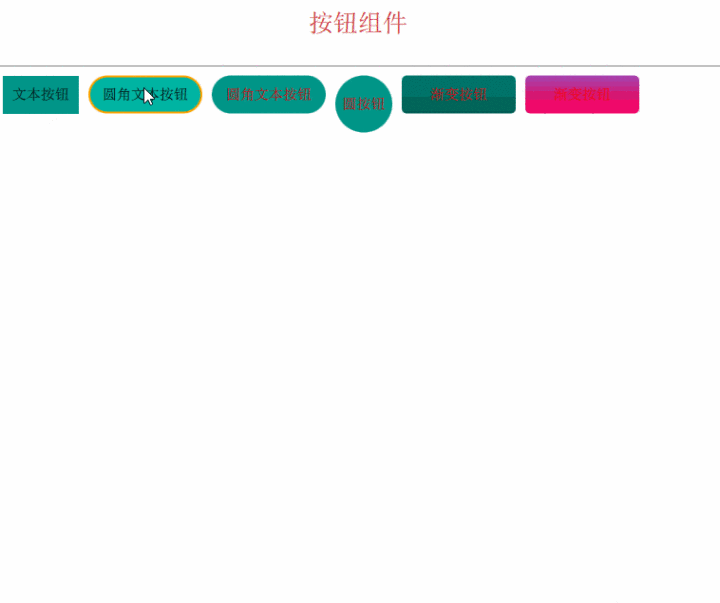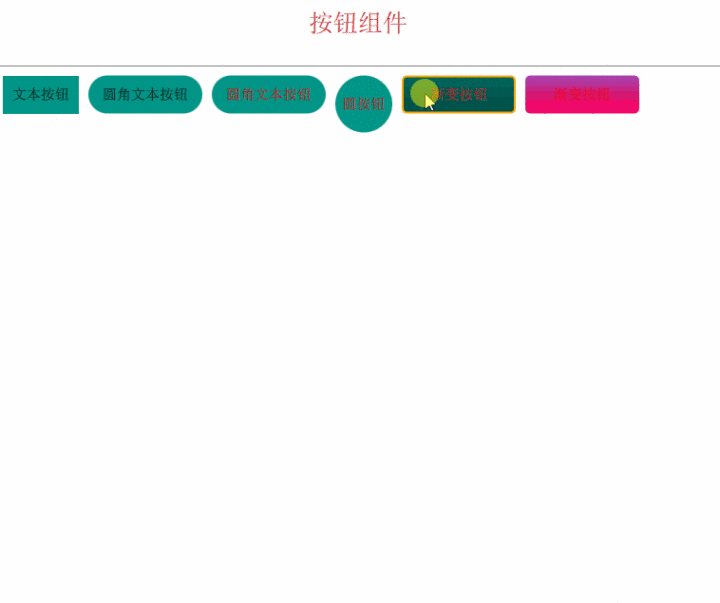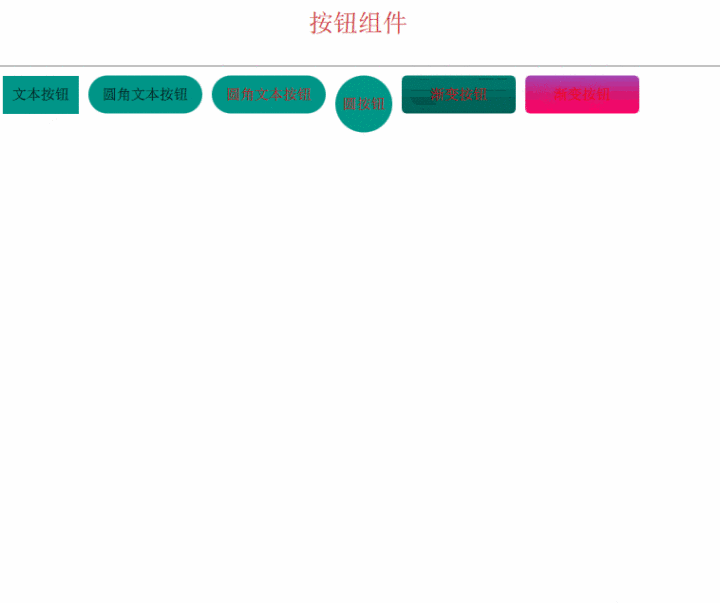
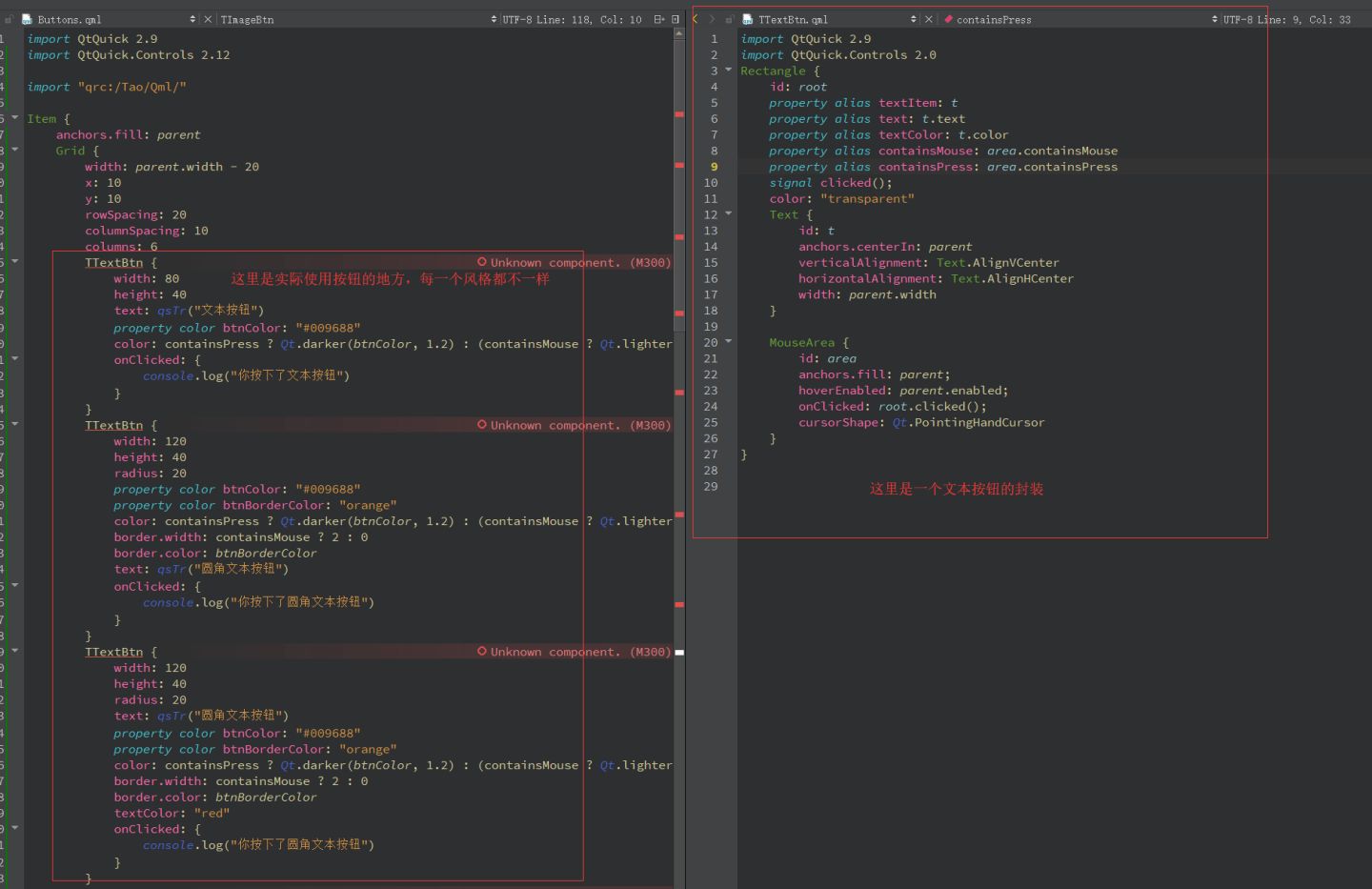
组件化按钮 为了能够复用我们的按钮,需要将它做成一个组件。
这里以文本按钮为例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 import QtQuick 2.9 import QtQuick.Controls 2.0 Rectangle { id: root property alias textItem : t property alias text : t.text property alias textColor : t.color property alias containsMouse : area.containsMouse property alias containsPress : area.containsPress signal clicked (); color : "transparent" Text { id: t anchors.centerIn : parent verticalAlignment : Text.AlignVCenter horizontalAlignment : Text.AlignHCenter width : parent .width } MouseArea { id: area anchors.fill : parent ; hoverEnabled : parent .enabled; onClicked : root.clicked(); cursorShape : Qt.PointingHandCursor } }
Qml组件,先以最简单的方式理解,就是放在一个单独的Qml文件中,声明一些属性导出,由使用者去实例化并设置属性
比如这样:
为了和标准的组件区分开,涛哥写的组件名字都以大写的T开头。
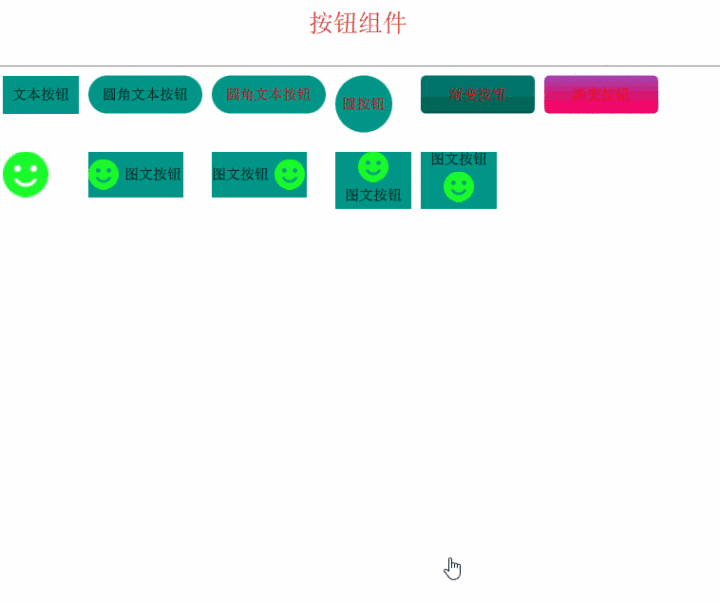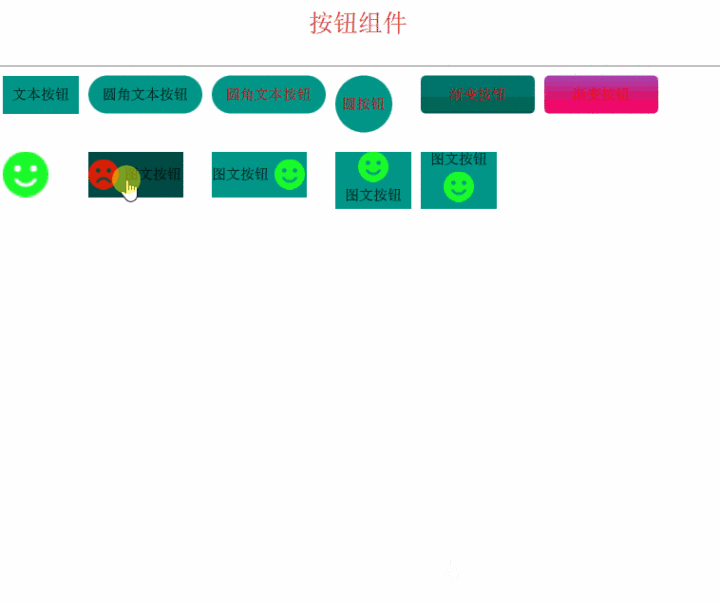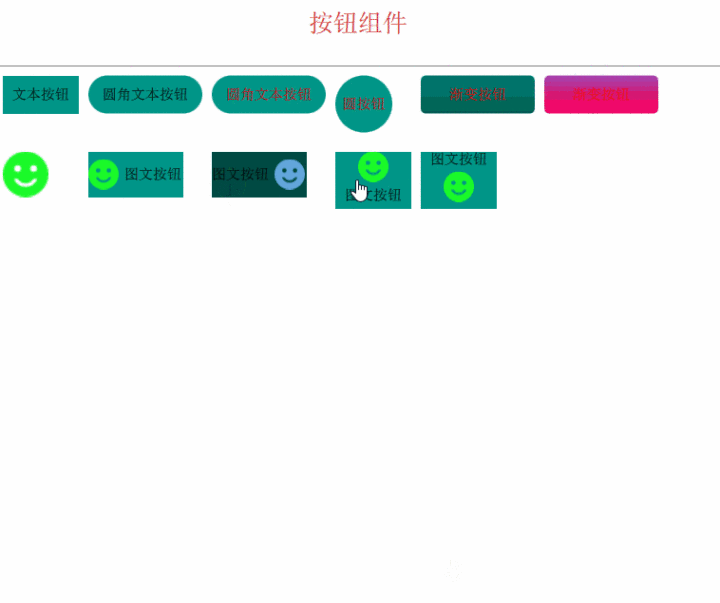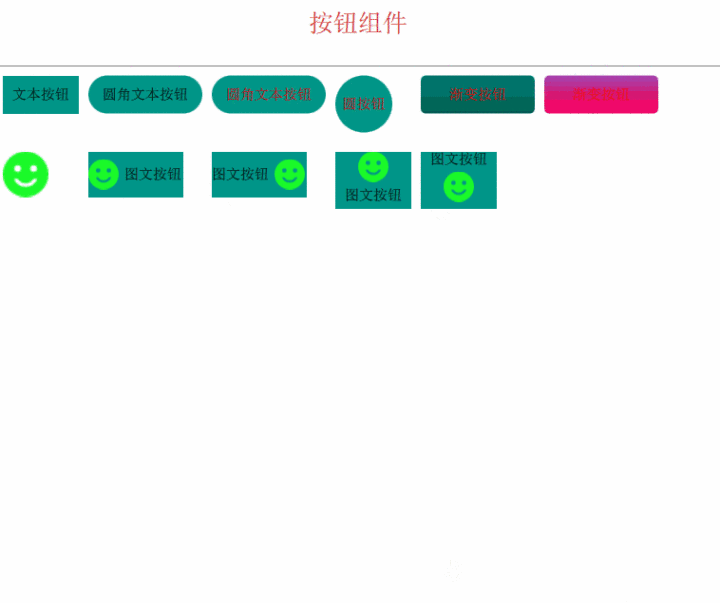
组件化的好处,包括容易复用(如上图,多个实例都不一样)、可以统一修改(后面会有动态换皮肤的方案,依赖于组件化)、
便于维护和扩展等。后续涛哥还会讲如何做多层抽象的组件、单例组件、如何引用插件中的组件等。
组件化图片按钮 带图片的按钮,只需要把Rectangle换成Image即可。
为了应对各种按钮状态,涛哥做了以下的属性扩展
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 import QtQuick 2.9 import QtQuick.Controls 2.0 Item { id: root property url normalUrl property url hoveredUrl property url pressedUrl property url disabledUrl property alias imageItem : img property alias imageUrl : img.source property alias imageWidth : img.width property alias imageHeight : img.height property alias imageAnchors : img.anchors property alias containsMouse : area.containsMouse property alias containsPress : area.containsPress signal clicked (); Image { id: img anchors.fill : parent source : root.enabled ? (containsPress ? pressedUrl : (containsMouse ? hoveredUrl : normalUrl)) : disabledUrl } MouseArea { id: area anchors.fill : parent ; hoverEnabled : parent .enabled; onClicked : root.clicked(); cursorShape : Qt.PointingHandCursor preventStealing : true } }
组件化图文按钮 有了前面的文字按钮和图片按钮,我们可以做一个图片和文字都有的按钮。
图片和文字同时显示,那么就有了布局问题。图片在左?还是在右?在上?还是在下?
涛哥这里用了点技巧,封装了一个同时支持四种布局的图文按钮
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 import QtQuick 2.9 import QtQuick.Controls 2.0 Rectangle { id: root property url normalUrl property url hoveredUrl property url pressedUrl property url disabledUrl property alias imageItem : img property alias imageUrl : img.source property alias imageWidth : img.width property alias imageHeight : img.height property alias textItem : t property alias text : t.text property alias textColor : t.color property alias containsMouse : area.containsMouse property alias containsPress : area.containsPress signal clicked (); property int layoutType : layoutImageLeft readonly property int layoutImageLeft : 0 readonly property int layoutImageRight : 1 readonly property int layoutImageUp : 2 readonly property int layoutImageDown : 3 color : "transparent" Image { id: img source : root.enabled ? (containsPress ? pressedUrl : (containsMouse ? hoveredUrl : normalUrl)) : disabledUrl } Text { id: t verticalAlignment : Text.AlignVCenter horizontalAlignment : Text.AlignHCenter } Component.onCompleted : { switch (layoutType) { case layoutImageLeft : img.anchors.verticalCenter = root.verticalCenter t.anchors.verticalCenter = root.verticalCenter img.anchors.left = root.left t.anchors.left = img.right t.anchors.leftMargin = 6 break ; case layoutImageRight : img.anchors.verticalCenter = root.verticalCenter t.anchors.verticalCenter = root.verticalCenter t.anchors.left = root.left img.anchors.left = t.right img.anchors.leftMargin = 6 break case layoutImageUp : img.anchors.horizontalCenter = root.horizontalCenter t.anchors.horizontalCenter = root.horizontalCenter img.anchors.top = root.top t.anchors.top = img.bottom t.anchors.topMargin = 6 break case layoutImageDown : img.anchors.horizontalCenter = root.horizontalCenter t.anchors.horizontalCenter = root.horizontalCenter t.anchors.top = root.top img.anchors.top = t.bottom img.anchors.topMargin = 6 break ; } } MouseArea { id: area anchors.fill : parent ; hoverEnabled : parent .enabled; onClicked : root.clicked(); cursorShape : Qt.PointingHandCursor } }
最后,我们来看看效果吧



 支付宝打赏
支付宝打赏
 微信打赏
微信打赏